Overview of Treatment of Adult Central Nervous System Tumors
There are different types of treatment for patients with adult brain and spinal cord tumors.
Five types of standard treatment are used:
- Active surveillance
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy
Supportive care is given to lessen the problems caused by the disease or its treatment.
New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials.
Treatment for adult central nervous system tumors may cause side effects.
Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial.
Patients can enter clinical trials before, during, or after starting their cancer treatment.
Follow-up tests may be needed.
Standard treatment Options
Active surveillance
Active surveillance is closely watching a patient’s condition but not giving any treatment unless there are changes in test results that show the condition is getting worse. Active surveillance may be used to avoid or delay the need for treatments such as radiation therapy or surgery, which can cause side effects or other problems. During active , certain exams and tests are done on a regular schedule. Active may be used for very slow-growing tumors that do not cause symptoms.
Surgery
Surgery may be used to diagnose and treat adult brain and spinal cord tumors. Removing tumor tissue helps decrease pressure of the tumor on nearby parts of the brain.
After the doctor removes all the cancer that can be seen at the time of the surgery, some patients may be given chemotherapy or radiation therapy after surgery to kill any cancer cells that are left. Treatment given after the surgery, to lower the risk that the cancer will come back, is called adjuvant therapy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body (systemic chemotherapy).
Brain is protected by a lining called the blood-brain barrier. Although most cannot, some chemotherapy drugs can cross the blood-brain barrier and reach tumor cells in the brain.
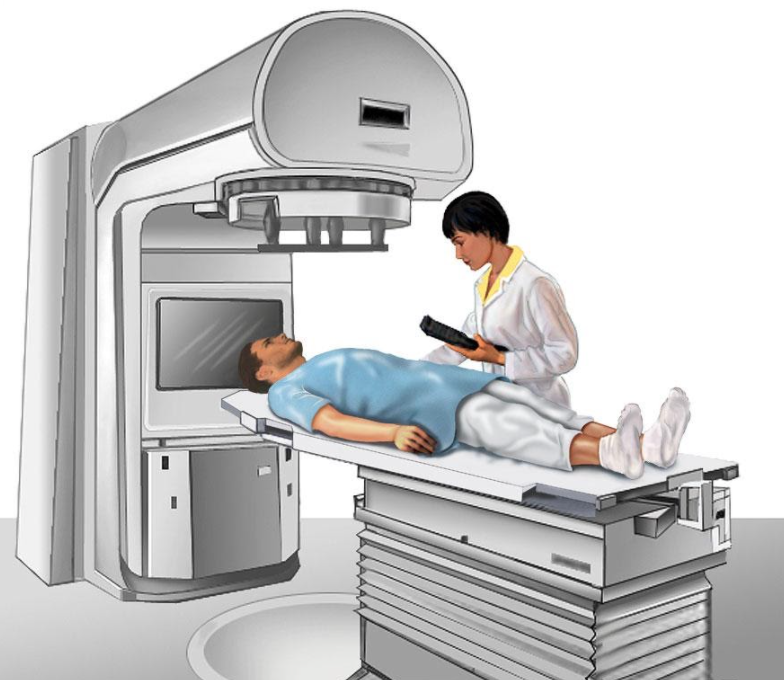
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the area of the body with cancer.
Certain ways of giving external radiation therapy can help keep radiation from damaging nearby healthy tissue. These types of radiation therapy include the following:
Conformal radiation therapy: Conformal radiation therapy uses a computer to make a 3-dimensional (3-D) picture of the tumor and shapes the radiation beams to fit the tumor.
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT): IMRT is a type of 3-dimensional (3-D) radiation therapy that uses a computer to make pictures of the size and shape of the tumor. Thin beams of radiation of different intensities (strengths) are aimed at the tumor from many angles.
Stereotactic radiosurgery: Stereotactic radiosurgery uses a rigid head frame that is attached to the skull to keep the head still during the radiation treatment. A machine aims a single large dose of radiation directly at the tumor. This procedure does not involve surgery. It is also called stereotaxic radiosurgery, radiosurgery, and radiation surgery.
Additional information can be found at: https://www.cancer.gov/types/brain/patient/adult-brain-treatment-pdq
